In our increasingly digital world, the shift away from traditional pen-and-paper signatures is undeniable.
Electronic contract signing has become the favored, and often mandatory, method of formalizing agreements. This shift toward electronic signatures brings efficiency, convenience, and a whole host of questions.
If you’re navigating the world of e-signature contracts, there are crucial points you should consider to ensure a smooth and legally sound process.
How Do E-Signatures Work?
The foundation of e-signature technology lies in Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
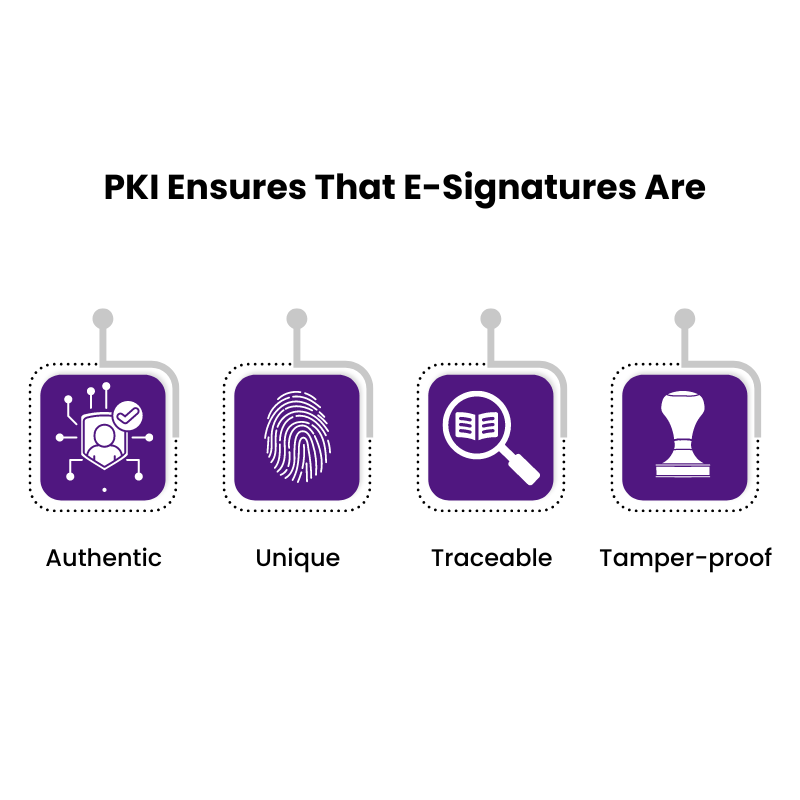
This system utilizes a cryptographic combination of private and public keys to securely encrypt and decrypt documents. PKI ensures that e-signatures are:
- Authentic: Each e-signature is linked to a unique digital identity, verifying the signer’s legitimacy.
- Unique: E-signatures cannot be copied or forged, guaranteeing they are one-of-a-kind.
- Traceable: The e-signature process leaves an unalterable trail, preventing signers from denying their involvement.
- Tamper-proof: The contents of a signed document and the associated e-signature cannot be modified after the signing process is complete.
To further bolster trust, PKI employs Certificate Authorities (CAs). These trusted third parties verify the identities of signers and their keys.
CAs can issue, validate, and even revoke certificates if needed, adding an additional layer of security to the e-signing process.
Now let’s delve into the essentials and best practices of how to sign contracts electronically.
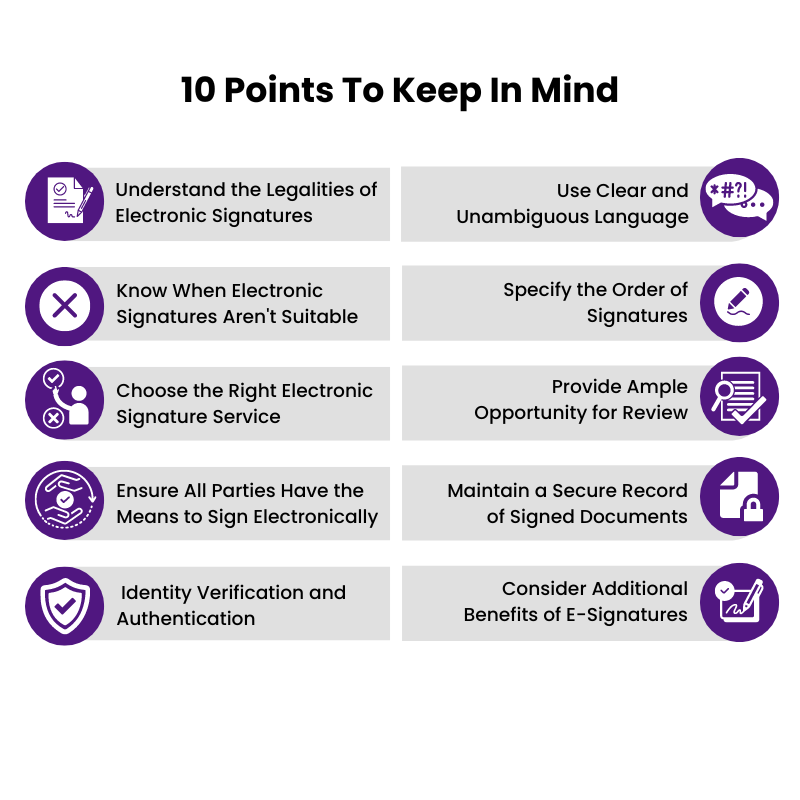
1. Understand the Legalities of Electronic Signatures
Before diving headlong into electronic contract signing, it’s vital to grasp the legality of it all. Fortunately, electronic signatures have robust legal backing in many countries.
Legislation such as the U.S. Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN Act) and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) solidify the validity of electronic signatures.
In essence, a properly executed e-signature carries the same weight as a handwritten one. This means you can confidently sign contracts online without the hassle of printing, physically signing, and then scanning or mailing documents.
2. Know When Electronic Signatures Aren’t Suitable
While incredibly versatile, electronic signatures do have limitations. Certain legally sensitive documents might require traditional notarization or witnessing, such as:
- Wills, trusts, and some estate planning documents
- Certain real estate or property transactions
- Documents relating to family law (divorce, adoptions, etc.)
Familiarize yourself with the specific laws in your jurisdiction to determine if there are cases where electronic signatures don’t suffice.
3. Choose the Right Electronic Signature Service
The market is full of platforms specializing in electronic signatures. Take the time to find one that meets your needs. Key factors to consider in your decision-making are:
- Security: Prioritize services with robust security protocols to protect your sensitive information.
- Ease of Use: A smooth user experience is crucial for all parties involved in signing contracts online.
- Feature Set: Assess if you need advanced features like templates, document tracking, or workflow automation.
- Pricing: Compare pricing models to find one that aligns with your signing volume and budget.
Technical Considerations
4. Ensure All Parties Have the Means to Sign Electronically
Not everyone is equally tech-savvy.
Before sending a document for e-signing, check if the other parties involved have access to the necessary devices and know how to sign a contract online. If needed, provide clear instructions or support to prevent delays.
5. Identity Verification and Authentication
Identity verification is crucial to ensuring the authenticity of e-signatures. Your chosen platform should offer various authentication methods to confirm the identity of signatories. Common options include:
- Email verification: Signers receive a code or link to their email to confirm access.
- SMS verification: A code is sent to the signer’s phone.
- Knowledge-based authentication (KBA):
Signers answer personal questions only they should know. - ID verification: Signers upload government-issued identification.
Best Practices

6. Use Clear and Unambiguous Language
A well-written contract is essential in both traditional and electronic formats. The language should be straightforward and leave no room for misinterpretation. Avoid overly complex legal jargon and strive for clarity.
When signing a contract online, it’s especially important that the agreement’s terms and conditions are readily accessible and understandable for all signers.
7. Specify the Order of Signatures
If multiple signatures are needed on an electronic contract, determine the signing order.
Your e-signature platform should facilitate this process, allowing you to designate who signs first, second, and so forth. This creates a smoother flow and eliminates confusion.
8. Provide Ample Opportunity for Review
Just as with a physical contract, allow all parties ample time to review the document thoroughly before signing a contract electronically. Rushing the process increases the risk of errors or misunderstandings. Make it clear that signers should take their time before applying their e-signatures.
9. Maintain a Secure Record of Signed Documents
Reliable e-signature services automatically generate and store audit trails of electronic signature contracts.
Ensure you have a secure system for keeping track of these digital contract signing events, proof of agreement, and for easily retrieving signed documents if needed. When choosing an e-signature service, consider how they handle document storage and how readily you can access your e-sign agreements.
10. Consider Additional Benefits of E-Signatures
Beyond legality and convenience, e-sign contracts offer further advantages. They can speed up the contract process, reduce errors, and potentially enhance your business’s environmental footprint.
Embracing electronic contract signing can streamline business processes and offer numerous advantages. By understanding the legal framework, technical requirements, and optimal practices, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the world of e-signatures with confidence.




