In today’s fast-paced business environment, building strong and ongoing relationships with reliable service providers is crucial for success. However, repeatedly negotiating the terms and conditions for each individual project or service engagement can be time-consuming and cumbersome, especially for busy small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
This is where MSAs (MSAs) come into play, offering a streamlined and efficient way to manage ongoing collaborations.
What is a Master Service Agreement?
A Master Service Agreement is a pre-negotiated, legally binding contract that establishes the foundational framework for multiple future engagements between a service provider and a client.
It serves as a template agreement, laying out the general terms and conditions that will govern all subsequent service engagements within the scope of the agreement.
Think of an MSA as a pre-approved blueprint that eliminates the need to renegotiate core terms for each project, saving you valuable time and resources. This streamlined approach offers several key benefits:
- Efficiency: No more starting from scratch for each project.
- Agreements can be negotiated and approved once for consistent application in future engagements.
- Standardized terms ensure consistency and avoid potential confusion or misinterpretations.
- Time Savings: Skip the repetitive process of negotiating basic terms repeatedly.
- Focus your time and energy on defining specific project details and deliverables.
- Expedite the service initiation process by having a pre-established framework.
- Cost Savings: Eliminate the need for repeated legal fees associated with individual contract negotiations.
- Both parties’ benefit from a more predictable and cost-effective approach to collaboration.
- Streamlined Communication: Focus on project specifics and collaboration, not contract legalese.
- Clear expectations foster smoother communication and project execution.
- Stronger Relationships: Establish a foundation for a trusting and long-term partnership.
- Predictable and efficient collaboration fosters mutual satisfaction and loyalty.
Beyond the core benefits mentioned above, MSAs offer several additional advantages :

- Reduced Risk: Clearly defined terms and conditions minimize the risk of disputes and misinterpretations.
- Flexibility: While the core framework is established, room exists for tailoring specific details for each individual project within the overall scope of the agreement.
- Scalability: MSAs are adaptable to various types of services and can grow alongside your business needs.
Overall, MSAs offer a valuable tool for SMBs to streamline their business operations, establish efficient collaboration models, and build strong, long-term relationships with their service providers.
By understanding the core aspects and benefits of MSAs, you can leverage their strengths to enhance your business efficiency and achieve greater success.
Understanding MSAs
In the dynamic world of business, collaboration with external service providers is essential for growth and success.
However, managing various service engagements can become complex, especially for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). This is where Master Service Agreements (MSAs) come into play, offering a strategic and efficient solution to streamline ongoing collaborations.
Purpose
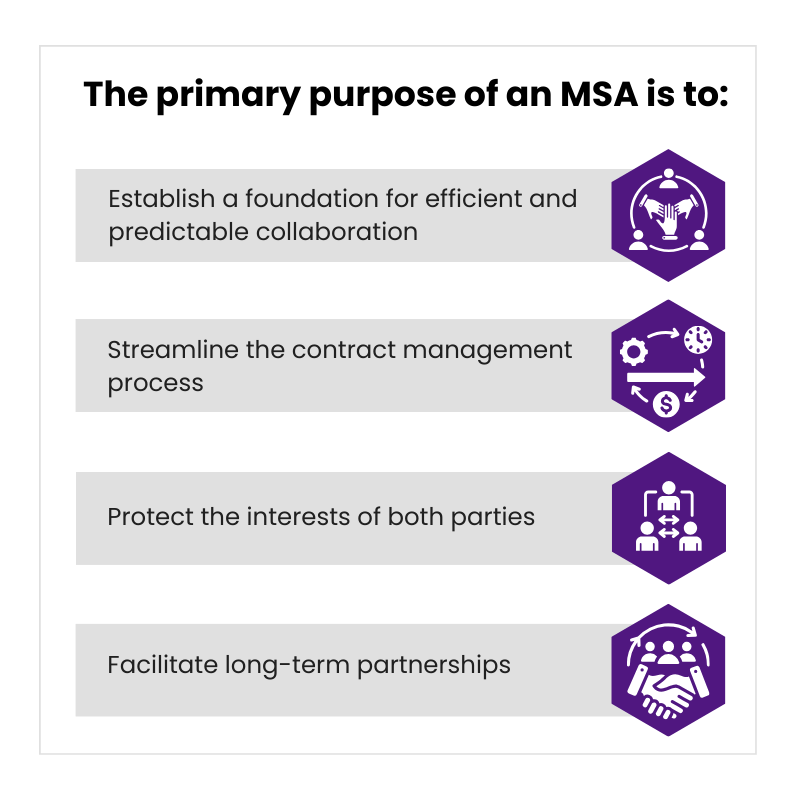
The primary purpose of an MSA is to:
- Establish a foundation for efficient and predictable collaboration: By pre-defining key terms and conditions, MSAs create a consistent and standardized framework for ongoing service engagements with the same provider. This fosters clarity, reduces ambiguity, and simplifies the process of initiating future projects.
- Streamline the contract management process: MSAs eliminate the need to repeatedly negotiate and draft individual contracts for each project, minimizing administrative burdens and associated costs. This allows businesses to focus on core activities and project execution.
- Protect the interests of both parties: A well-crafted MSA outlines the rights and responsibilities of both the service provider and the client, minimizing the risk of misunderstandings and disputes. This promotes a fair and transparent framework for collaboration.
- Facilitate long-term partnerships: By establishing a foundation of trust and clear expectations, MSAs can pave the way for strong and lasting partnerships with service providers. This facilitates a collaborative and mutually beneficial business environment.
By understanding the definition and purpose of MSAs, SMBs can leverage this versatile tool to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce administrative overheads, and build stronger relationships with their service providers, ultimately contributing to their long-term success in the competitive business landscape.
Key Components of MSAs
An MSA typically covers various essential elements:
#1. Scope of Work
The scope of work is arguably the most crucial component of an MSA, as it clearly defines the services to be provided, deliverables expected, and responsibilities of each party.

A well-defined scope of work helps avoid misunderstandings, delays, and potential disagreements down the road. Here’s what a comprehensive scope of work should encompass:
- Detailed Description of Services: This section should clearly outline the specific services the service provider will offer. Be as specific as possible and avoid using ambiguous language.
- Deliverables: Clearly define the expected deliverables for each service, including format, timeline, and quality standards.
- Responsibilities : Define the specific tasks and obligations of both parties involved in the agreement. This includes outlining what the service provider is responsible for delivering and what the client is expected to provide (e.g., information, resources, access).
- Acceptance Criteria: Establish clear criteria for accepting deliverables, ensuring both parties are on the same page about the expected quality and completeness.
- Changes to the Scope: Outline the process for making changes to the scope of work, including requiring written documentation and potential cost adjustments.• Changes to the Scope: Outline the process for making changes to the scope of work, including requiring written documentation and potential cost adjustments.
#2. Payment Terms

The payment terms section of an MSA specifies how the service provider will be compensated for their services. It defines a clear and transparent payment structure to avoid any financial disputes in the future. Here are some key elements of this section:
- Payment Schedule: Clearly outline the payment schedule, including the frequency of payments (e.g., monthly, quarterly) and any milestone payments linked to specific deliverables.
- Invoicing Procedures: Specify the format and delivery method for invoices, including deadlines for payment and any applicable late payment penalties.
- Payment Methods: Define the acceptable methods of payment (e.g., bank transfer, check, credit card).
- Taxes and Other Fees :Clarify who is responsible for paying any applicable taxes, fees, or surcharges.
#3. Duration and Termination
The duration and termination clause defines the timeframe of the agreement and the process for either party to terminate the agreement under specific circumstances. Here’s what this section should address:
- Term: Specify the initial term of the agreement, which can be fixed (e.g., one year) or open-ended with an automatic renewal clause based on mutual agreement.
- Renewal Options: If applicable, outline the conditions for automatic or optional renewal of the agreement.
- Termination Clause: Define the grounds for termination by either party, including circumstances like breach of contract, financial hardship, or insolvency.
- Notice Period: Specify the required notice period for either party to initiate termination.
- Termination Process: Outline the steps involved in the termination process, including any specific procedures or requirements.
#4. Confidentiality Clauses

Confidentiality clauses safeguard sensitive information shared during the collaboration and protect the intellectual property of both parties. It ensures that confidential information is not misused or disclosed to unauthorized individuals or entities.
A robust confidentiality clause should encompass the following:
- Definition of Confidential Information: Clearly define what constitutes confidential information, including customer information, trade secrets, financial data, and intellectual property.
- Non-Disclosure Obligations: Both parties agree not to disclose confidential information to any unauthorized third party without prior written consent.
- Exceptions: If any exceptions exist to the non-disclosure obligation (e.g., legally required disclosure), they should be explicitly stated.
- Confidentiality Term: Specify the duration for which the confidentiality obligations remain in effect, even after the agreement terminates.
- Remedies for Breach: Outline the consequences of breaching the confidentiality clause, which may include legal action, damages, or injunctive relief.
By meticulously addressing these key components, you can ensure your MSA establishes a clear and comprehensive framework for collaboration, protecting your interests and fostering a successful business relationship.
Benefits of MSAs
MSAs (MSAs) offer a valuable tool for businesses, particularly SMBs, to streamline collaborations and protect their interests. Here’s a detailed look at the key benefits of implementing MSAs:
#1. Risk Mitigation
- Reduced Misunderstandings: MSAs establish a clear and predictable framework for ongoing collaborations, minimizing the risk of misunderstandings and misinterpretations of terms and conditions. This clarity helps prevent disputes and potential legal implications.
- Defined Responsibilities: By outlining the roles and responsibilities of each party in detail, MSAs clarify expectations and avoid ambiguity regarding service delivery, payment obligations, and intellectual property ownership. This minimizes the chance of conflicts arising from unclear or undocumented expectations.
- Controlled Risks: MSAs allow for the inclusion of specific clauses addressing potential risks, such as confidentiality breaches, service disruptions, or termination procedures. This proactive approach helps anticipate and manage potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
#2. Cost Savings
- Reduced Negotiation Costs: By establishing a pre-negotiated framework, MSAs eliminate the need for extensive re-negotiation of basic terms and conditions for each individual project with the same service provider. This translates to significant time and cost savings for both parties.
- Streamlined Contract Management: MSAs centralize key contract information in a single document, reducing administrative overhead associated with managing multiple individual contracts for each service engagement. This streamlined approach minimizes resource allocation and associated costs.
- Predictable Pricing: MSAs often offer predefined pricing structures or billing rates for services, providing greater clarity and predictability compared to negotiating variable rates for each engagement. This allows for improved budget planning and cost control.
#3. Streamlined Processes
- Efficient Onboarding: Having a pre-approved MSA in place allows for quicker onboarding of new projects with the same service provider. This eliminates the need for lengthy contract negotiation and approval processes, allowing for faster project initiation.
- Standardized Collaboration: MSAs establish a consistent baseline for collaboration across multiple projects, ensuring all parties understand the expectations and procedures. This promotes standardized work practices and reduces the need for repetitive re-explanations for each new project.
- Improved Communication: Pre-defined terms and conditions foster clearer communication between the service provider and the client. This allows for a more productive and focused discussion on specific project details without getting bogged down in contract legalese.
By leveraging the benefits of MSAs, SMBs can operate with greater efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and ultimately achieve increased profitability.
Additionally, the enhanced clarity and reduced risk associated with MSAs create a more stable and secure foundation for building long-term, trusted partnerships with service providers.
Common Mistakes in Drafting MSAs

While MSAs (MSAs) offer a plethora of benefits for businesses, including streamlined collaboration and reduced costs, pitfalls lurk in the drafting process. Here’s a closer look at some common mistakes to avoid when creating your MSA:
#1. Ambiguous Language
- Impact: Leaving room for interpretation can lead to misunderstandings and disputes down the line.
- Solution: Use clear, concise, and plain language that is easily understandable by both parties. Avoid technical jargon or legalistic terms that may be confusing.
- Example: Instead of “The service provider shall deliver the services in a timely manner,” specify a concrete timeframe for deliverables.
#2. Inadequate Scope Definition
- Impact: An incomplete or unclear scope definition can lead to disagreements about what services are included or excluded, potentially causing delays and additional costs.
- Solution: Clearly and comprehensively define the scope of work, including the specific services to be provided, deliverables expected, and any limitations.
- Use detailed descriptions and avoid leaving room for ambiguity.
- Example: Instead of “The service provider will provide marketing services,” specify the types of marketing services included (e.g., content creation, social media management, email marketing).
#3. Lack of Clear Payment Terms
- Impact: Unclear payment terms can lead to confusion, financial disputes, and potential delays in receiving payment.
- Solution: Clearly outline the payment schedule, including the frequency of payments, invoicing procedures, and any applicable late payment penalties. Specify the payment method (e.g., bank transfer, credit card) and the currency used.
- Example: Instead of “Payment will be due upon completion of the services,” specify the due date for invoices and the consequences of late payment (e.g., interest charges).
Additional Tips for Avoiding Drafting Pitfalls

- Seek legal counsel: Consulting with a lawyer experienced in contract law can help you draft a comprehensive and legally sound MSA that protects your business interests.
- Use clear and consistent formatting: Ensure the MSA is easy to read and navigate by using clear formatting, numbering sections, and including a table of contents.
- Outline change management procedures: Specify the process for making amendments or revisions to the agreement to ensure both parties agree to any changes.
- Review thoroughly before signing: Carefully review the entire MSA with all involved parties before signing to ensure it accurately reflects your understanding and captures all necessary details.
By understanding and avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can draft effective and well-defined MSAs that facilitate smooth collaboration, minimize risks, and contribute to a successful and productive working relationship with their service providers.
Key Terms in MSAs
MSAs provide a framework for ongoing collaborations with service providers. However, they are legal documents containing crucial terms that require careful understanding. Here, we delve into three key terms you’ll encounter in most MSAs:
#1. Indemnification
- Definition: This clause outlines which party is financially responsible for covering costs or damages arising from the agreement’s performance.
- Purpose: It allocates risk and protects both parties from potential financial losses caused by the actions or omissions of the other party during the service engagement.
- Scenarios:
- Client Indemnification: The client may agree to indemnify the service provider for claims arising from the client’s own negligence or misuse of the services.
- Service Provider Indemnification: The service provider may be responsible for indemnifying the client for losses due to their own negligence, breach of contract, or intellectual property infringement.
- Importance: Understanding the indemnification clause is crucial to assessing your potential financial exposure under the agreement.
#2. Limitation of Liability
- Definition: This clause sets a maximum limit on the number of damages that either party can be held liable for in case of a breach of contract or other legal claims arising from the agreement.
- Purpose: It aims to manage and mitigate potential financial risks associated with unforeseen circumstances or unforeseen damages.
- Considerations:
- Types of limitations: The clause may limit liability to specific categories of damages (e.g., direct damages) or set a capped dollar amount.
- Varying limitations: Different limits may apply depending on the type of breach or the nature of the claim.
- Importance: Recognizing the limitations of liability helps you understand the extent of your potential financial recovery in case of disputes or breaches.
#3. Governing Law and Dispute Resolution
- Definition: This clause specifies the legal jurisdiction (state or country) whose laws will apply to interpret and enforce the agreement in case of disputes. It also outlines the mechanism for resolving disagreements between the parties.
- Purpose: It ensures that both parties are aware of the legal framework governing the agreement and the process for resolving any conflicts that may arise.
- Mechanisms for Dispute Resolution
- Negotiation: The most common approach, where both parties attempt to reach a mutually agreeable solution through discussion and compromise.
- Mediation: A neutral third party facilitates communication and helps reach a settlement.
- Arbitration: A neutral third party makes a binding decision on the dispute, which is typically faster and less expensive than litigation.
- Importance: Knowing the governing law and dispute resolution mechanism helps you understand how potential conflicts will be addressed and the legal framework under which the agreement will be interpreted and enforced.
By comprehending these key terms and their implications, you can engage in informed decision-making while negotiating and entering into MSAs. Remember, it’s crucial to consult with legal counsel to ensure you fully understand the specific terms and how they apply to your unique business situation.
Best Practices for MSAs

Negotiating MSAs (MSAs) can be a complex process, but with the right strategies, you can ensure a win-win outcome for both your business and the service provider. Here, we explore three key aspects of successful MSA negotiation:
#1. Preparation Strategies
- Thorough Understanding of Needs: Before entering negotiations, clearly define your business needs and expectations for the service engagement. This includes identifying the specific services required, desired deliverables, and preferred timelines.
- Research the Service Provider: Conduct thorough research on the service provider, including their reputation, experience, expertise, and standard contract terms. This knowledge equips you to negotiate from a position of strength and assess their approach to collaborations.
- Review Industry Benchmarks: Research industry benchmarks for typical terms and conditions associated with similar services. This knowledge allows you to establish a realistic baseline for your negotiation efforts.
#2. Effective Communication
- Clear and Concise Communication: Throughout the negotiation process, maintain clear and concise communication with the service provider. Express your needs and expectations explicitly and listen actively to their perspective.
- Focus on Collaborative Approach: Strive for a collaborative and respectful discussion rather than an adversarial one. This fosters a more positive environment for reaching mutually beneficial agreements.
- Address Key Concerns Early: Identify and address key concerns or potential deal-breakers upfront to avoid wasting time negotiating on minor points that can be readily resolved.
#3. Win-Win Negotiation Techniques
- Focus on Value Creation: Focus on mutually beneficial outcomes that create value for both parties. Consider the service provider’s needs and explore creative solutions that address both your requirements and theirs.
- Negotiate with Empathy: Recognize that the service provider also has interests and concerns. By approaching the negotiation with empathy and understanding, you’re more likely to reach a solution that is satisfactory for both parties.
- Be Prepared to Walk Away: While reaching an agreement is desirable, it’s crucial to be prepared to walk away if the terms are not ultimately in your best interest. This demonstrates your commitment to securing a fair and balanced agreement.
By following these best practices and utilizing effective contract negotiation techniques, you can approach MSA negotiations with confidence and secure agreements that foster successful and long-term collaborations with your service partners.
Remember, the goal is to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes that contribute to your business goals and ensure a productive working relationship.
Additional Reading: Successful MSA Implementation Case Studies
Case Study 1: Streamlining Operations with MSAs – Tech Startup and Marketing Agency
Challenge: A young tech startup, InnoTech, was experiencing growing pains as they signed numerous short-term contracts with various marketing agencies for specific campaigns. This resulted in repetitive contract negotiation, inefficient project management, and limited visibility into overall marketing spend.
Solution: InnoTech implemented MSAs (MSAs) with their preferred marketing agencies. The MSAs outlined standardized terms and conditions for all future collaborations, including pricing structures, service levels, intellectual property ownership, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Benefits
- Reduced Negotiation Time: Pre-defined terms in the MSA eliminated the need for lengthy negotiations for each project, saving significant time and resources for both InnoTech and the agencies.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlined project management with consistent processes and clear expectations outlined in the MSA.
- Enhanced Visibility: Centralized information within the MSA provided InnoTech with a clearer picture of their overall marketing spend and agency performance.
Take aways
- MSAs are particularly beneficial for businesses with recurring collaborations with the same service providers.
- Clearly defined terms and conditions in the MSA minimize ambiguity and potential for disputes.
- Regularly reviewing and updating MSAs ensures they remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Case Study 2: Building Long-Term Partnerships with MSAs – Retail Chain and Logistics Provider
Challenge: A large retail chain, MegaMart, was facing challenges with inconsistent service levels and unpredictable costs from their various logistics providers due to short-term contracts. This hampered their ability to plan effectively and optimize supply chain efficiency.
Solution: MegaMart implemented MSAs with pre-approved logistics providers, establishing a framework for long-term collaboration. The MSAs included provisions for performance-based incentives, aligning the provider’s success with MegaMart’s business goals.
Benefits
- Improved Service Consistency: Standardized processes and performance metrics outlined in the MSA ensured consistent and reliable service delivery from the logistics providers.
- Cost Optimization: Competitive pricing structures and volume discounts within the MSA led to more predictable and manageable logistics costs for MegaMart.
- Stronger Partnerships: The long-term commitment fostered by the MSAs encouraged collaboration and open communication between MegaMart and their logistics partners, leading to continuous improvement and innovation within the supply chain.
Take aways
- MSAs can be used to establish long-term, strategic partnerships with key service providers.
- Performance-based incentives can be incorporated into MSAs to align service provider’s goals with the client’s business objectives.
- MSAs can foster open communication and collaboration between businesses and their service providers.

![A Definitive Guide to Master Service Agreement (MSA) [Free Template Included]](https://vyapi.com/wp-content/uploads/A-Guide-to-MSA.png)


